The Checks activity returns a boolean value for a validation check of a number.
uses System.Math
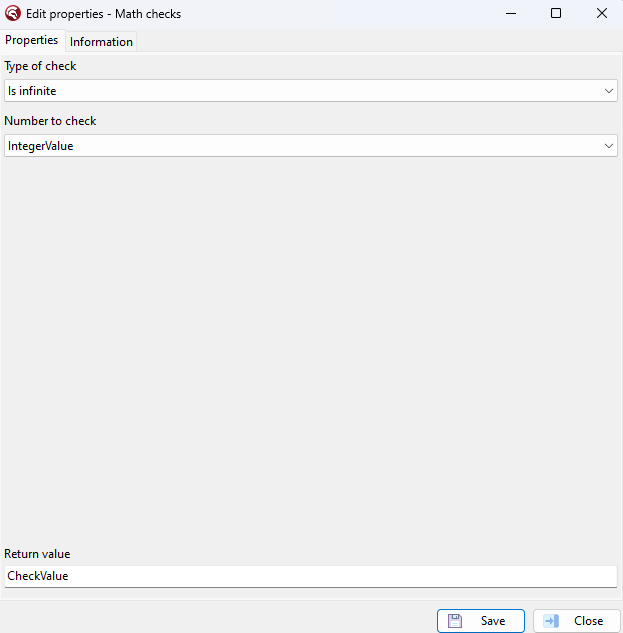
Activity properties
Possible checks:
Indicates when a variable represents an infinite value.
Example:
IntegerValue = 10
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; CheckValue := IsInfinite(IntegerValue); end; |
Result = False
Indicates when a variable represents a 'Not a number' (Nan) value.
Example:
IntegerValue = 10
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; CheckValue := IsNan(IntegerValue); end; |
Result = False
Indicates when a floating-point variable or expression evaluates to zero with a deviation.
Example:
DecimalValue = 0.5
Deviation = 1
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; CheckValue := IsZero(DecimalValue, 1); end; |
Result = True
Indicates whether two floating-point values are equal. with a possible deviation.
Example:
IntegerValue =2
DecimalValue = 0.5
Deviation = 1
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; CheckValue := SameValue(DecimalValue, IntegerValue, 1); end; |
Result = False
Indicates whether a numeric value is positive.
Example:
IntegerValue = 10
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; var SignValue := Sign(IntegerValue); CheckValue := SignValue = TValueSign(PositiveValue); end; |
Result = True
Indicates whether a numeric value is negative.
Example:
IntegerValue = 10
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; var SignValue := Sign(IntegerValue); CheckValue := SignValue = TValueSign(NegativeValue); end; |
Result = False
Indicates whether a value falls within a specified range.
Example:
IntegerValue = 2
MinRange = 1
MaxRange = 3
begin var CheckValue: Boolean; CheckValue := InRange(IntegerValue, 1, 3); end; |
Result = True
Providing a higher minimum than maximum is possible, but is also never true.